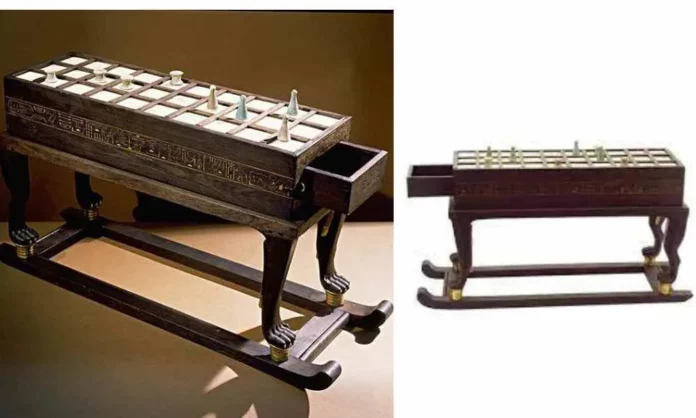
When we think about ancient Egypt, images of grand pyramids, golden treasures, and mystical gods often come to mind. But the discovery of a beautifully crafted Senet board in the tomb of Tutankhamun has opened a new window into the leisure activities of the ancient pharaohs. More than just a game, Senet held deep cultural and religious significance. Let’s explore the rich history and meaning behind this ancient artifact.
A Game of Antiquity: Over 2,000 Years Old
Senet is not just a relic; it’s one of the oldest board games in human history, dating back over 2,000 years. Both the Egyptian elite and commoners enjoyed playing Senet, but the game was especially favored by royalty. The Senet board found in Tutankhamun’s tomb, crafted from ebony and ivory and resting on elegant animal-shaped legs, is a prime example of the luxury and craftsmanship associated with the pharaoh’s leisure activities.
This artifact, discovered in the Valley of the Kings, is a visual reminder that entertainment has always been a part of human civilization, even for the rulers of ancient Egypt.
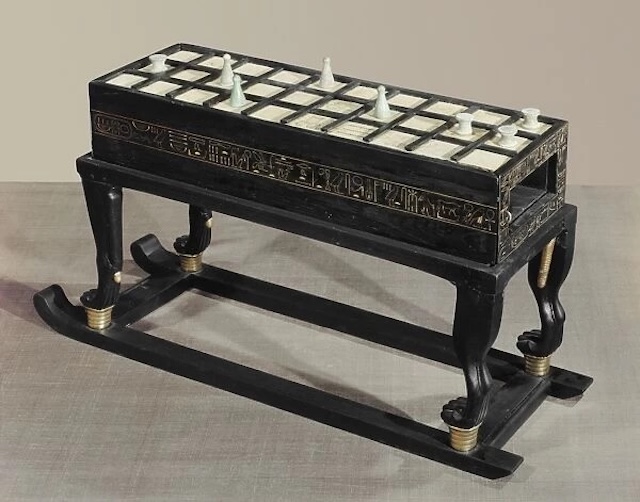

More Than Just a Game: The Spiritual Meaning of Senet
Senet wasn’t just about passing time; it carried a deeper spiritual significance. In Egyptian belief, Senet symbolized the journey of the soul through the afterlife. Egyptians believed that after death, a person would play a game of Senet against the gods, which would determine their fate in the afterlife. The game represented a symbolic battle between good and evil, with the outcome dictating whether the soul could successfully pass into the afterlife.
Tutankhamun’s tomb even features artwork showing the young pharaoh playing Senet with his queen, Nefertari. This suggests that the game held not only entertainment value but also spiritual importance, reflecting the eternal connection between life and the afterlife.
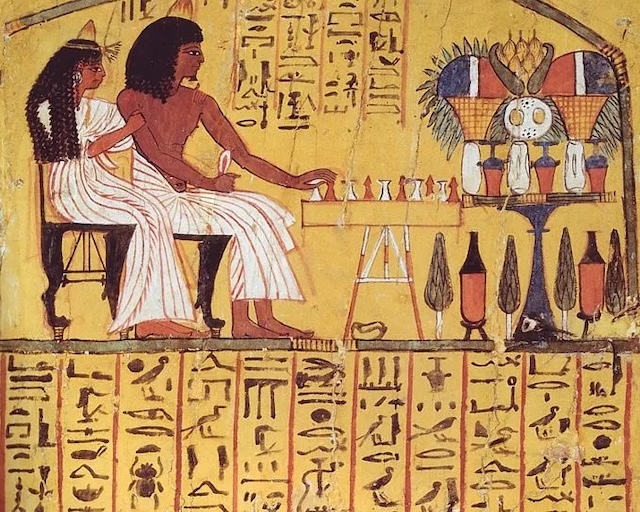
How to Play: The Basics of the Senet Game
While many of the rules have been lost to time, historians have reconstructed some of the basics of Senet. The game board consists of 30 squares, arranged in three rows of ten. Players moved their pieces across the board by throwing small, four-sided sticks, similar to modern dice. The goal was to navigate the board and be the first player to reach the end, representing the passage of the soul into the afterlife.
The simplicity of the game’s structure—combined with its complex spiritual symbolism—suggests that Senet was much more than a mere pastime for the ancient Egyptians.
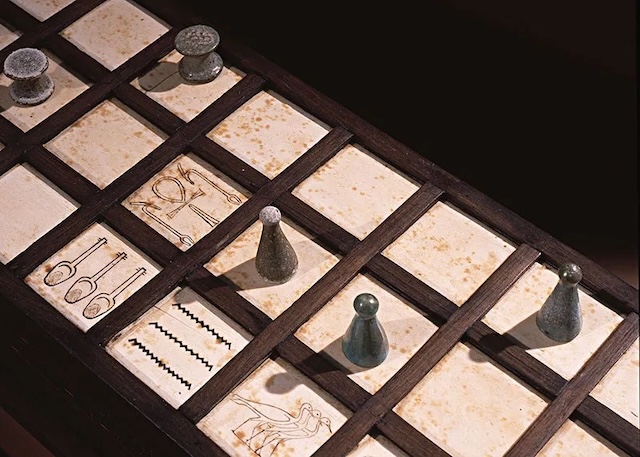

A Window Into the Past: What the Senet Board Reveals
The Senet board found in Tutankhamun’s tomb isn’t just a fascinating piece of history; it’s a direct link to the personal life of one of Egypt’s most famous pharaohs. It reveals that beyond ruling and warfare, even ancient kings had moments of play and relaxation. More importantly, the game demonstrates how entertainment in ancient Egypt was often intertwined with religion, offering a glimpse into the cultural mindset of the time.
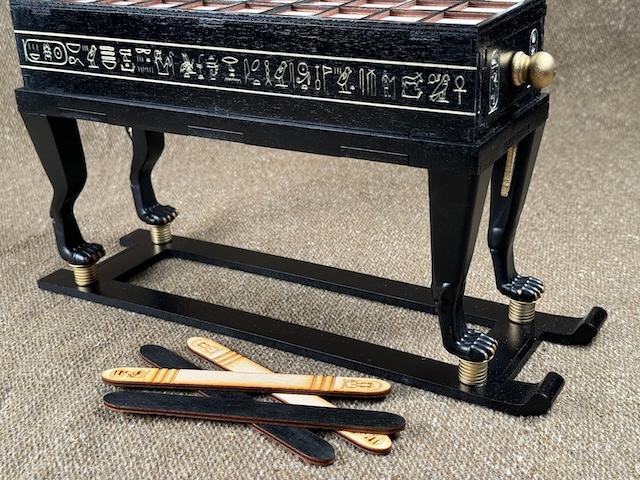

Conclusion
The Senet game board from Tutankhamun’s tomb is a remarkable discovery that sheds light on the leisure, culture, and spiritual beliefs of ancient Egyptians. This artifact serves as both a historical and religious symbol, revealing that even in their leisure activities, Egyptians were deeply connected to the spiritual journey of life and the afterlife. Whether seen as a simple board game or a ritualistic practice, Senet remains one of the most fascinating pieces of Egypt’s ancient history.
